之前介绍过串口通讯,相对来说串口通讯是比较简单的,不用关心另外一端的连接状态,只需要打开串口,监听接收事件即可。发送也很简单,一个Write方法控制。
但是串口的问题也很明显,我们无法得知另外一端是否可用,只能通过通讯协议里进行指定,设置心跳包或者指定接收后进行响应。打开监听简单,但是维持监听判断监听状态就相对麻烦一些。
对于开发来说,Socket通信(网口)要麻烦一些,因为需要了解TCP/UPD协议,还区分了服务端与客户端,但是硬件连入局域网就可以通信,所以使用Socket通信也是一种主流的解决方案。
关于基础的知识比如什么是Socket通信,什么是TCP协议,这里也不做展开,有兴趣的可以自己搜索相关资料了解。
Socket通信调试工具
个人使用较多的是TCP/UDP Socket 调试工具。
使用中可能存在的一些问题:
- 偶发关闭了另外一端,会导致调试工具异常;
- 编码默认本地字符集,所以经常导致中文乱码,需要收集16进制自行解析编码;
- 在收集数据的时候,接收区会添加接收的时间,解析时需要我们自己将这些字符替换掉;
当然这些基本也不会影响我们的调试工作。
单客户端
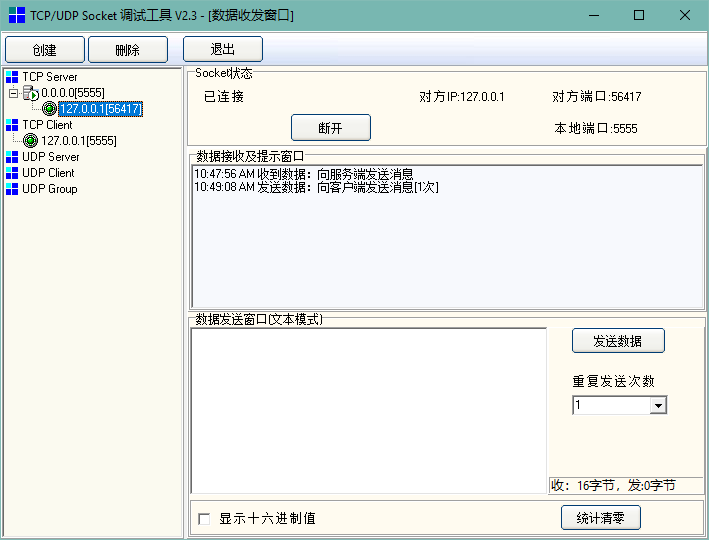
首先我们使用调试工具进行模拟,调试工具中创建一个TCP Server,监听端口根据自己需求设置。因为我们没有监听指定端口的需求,只是进行模拟测试,我们这里设置监听5555端口进行测试:
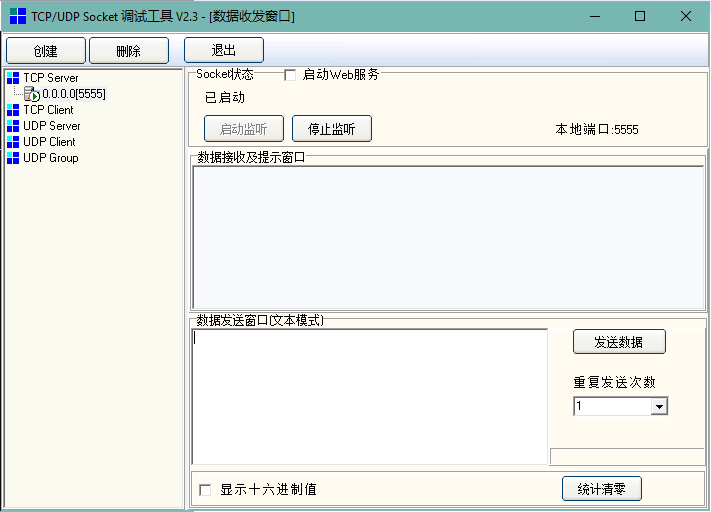
如上图,创建的TCP Server自动启动了监听。
服务端创建成功,我们就需要创建一个客户端进行连接,来进行数据的通讯,同样的我们选择TCP Client进行创建,并连接到本机的5555端口:
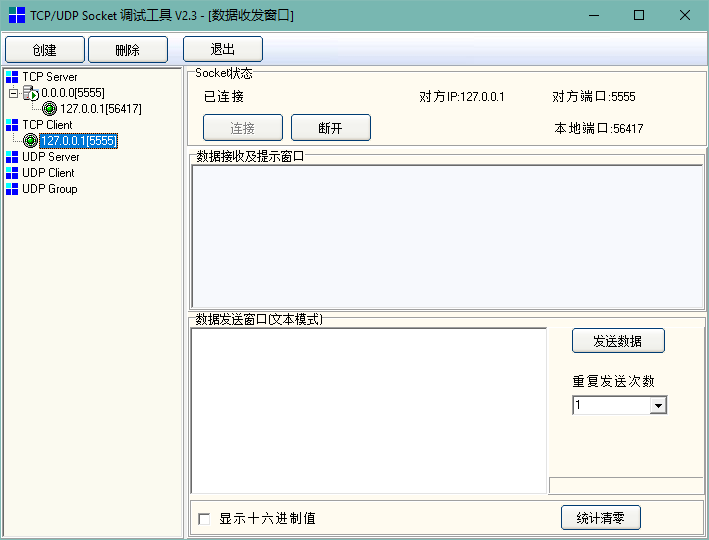
这时我们就可以点击TCP Client下打开的客户端向服务端发送消息,或选择TCP Server服务端下连接的客户端,向指定客户端发送消息:
那么,我们应该怎样在程序中打开服务端,监听客户端请求呢?可以参考以下代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SocketTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TcpServerTest.Test();
}
}
public static class TcpServerTest
{
public static void Test()
{
// 服务端地址默认本地
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
// 提醒用户输入要监听的端口
Console.Write("请输入您要监听的端口:");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int port;
while (!int.TryParse(input, out port))
{
Console.Write("您输入的端口错误,请重新输入:");
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
try
{
// 创建并打开监听
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(address, port);
listener.Start();
ConsoleLogger.Info($"启用服务端 {listener.Server.LocalEndPoint} 成功,等待客户端连接。");
// 等待客户端的连接请求
TcpClient client = listener.AcceptTcpClient();
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端连接成功:{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()}");
// 建立与客户端的数据流
using NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];//设置缓存长度
while (true)
{
try
{
int length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
if (length > 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]接收到数据: {Console.InputEncoding.GetString(buffer, 0, length)}");
// 回发接收到的消息给客户端
client.Client.Send(buffer, 0, length, SocketFlags.None);
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]关闭");
break;
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]引发未处理异常:{exc.Message}");
break;
}
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"TCP服务端测试出现了未经处理的异常:{exc.Message}");
}
ConsoleLogger.Info("测试结束");
}
}
public class ConsoleLogger
{
private static readonly object sync = new object();
public static void Error(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} Error: {message}");
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
public static void Info(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} Info: {message}");
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
}
}
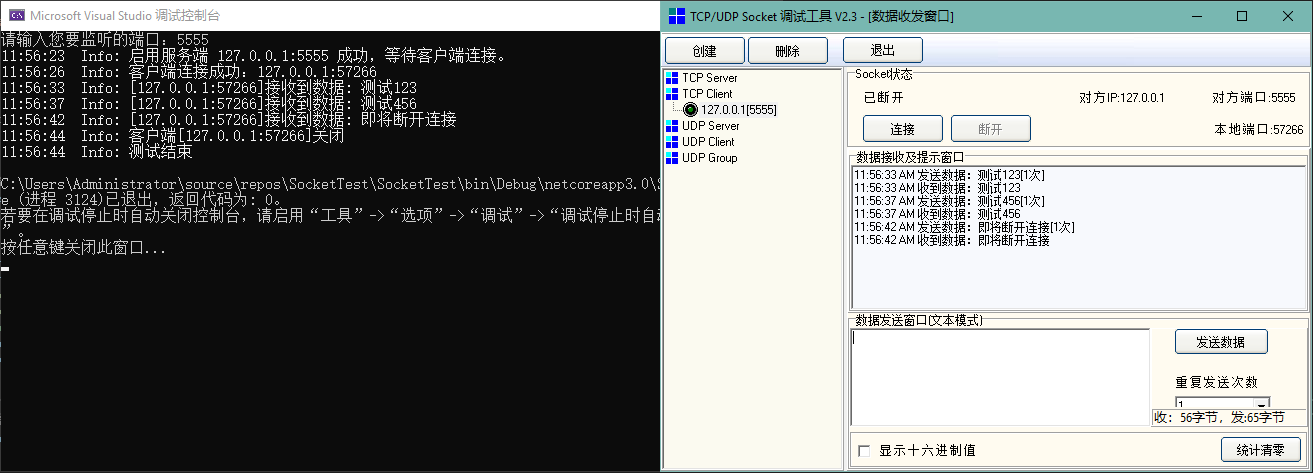
如上例子展示了一个服务端的创建与监听过程,连接成功后如果接收到客户端的消息,“复读”该消息发送给客户端。
我们可以进行测试,首先运行项目,在控制台创建服务端,并开启监听。服务端创建成功后,使用Socket的调试工具创建一个TCP客户端,与服务端进行通讯测试,结束后断开连接:
多客户端连接
如上例子正如测试结果一样,只能接受一个客户端的连接,当该客户端连接成功后,其他客户端如果再申请与服务端进行连接,虽然不会被拒绝,但是发送消息将无法获得响应。
关于如何建立与多个客户端连接,这里有两种方案。
循环
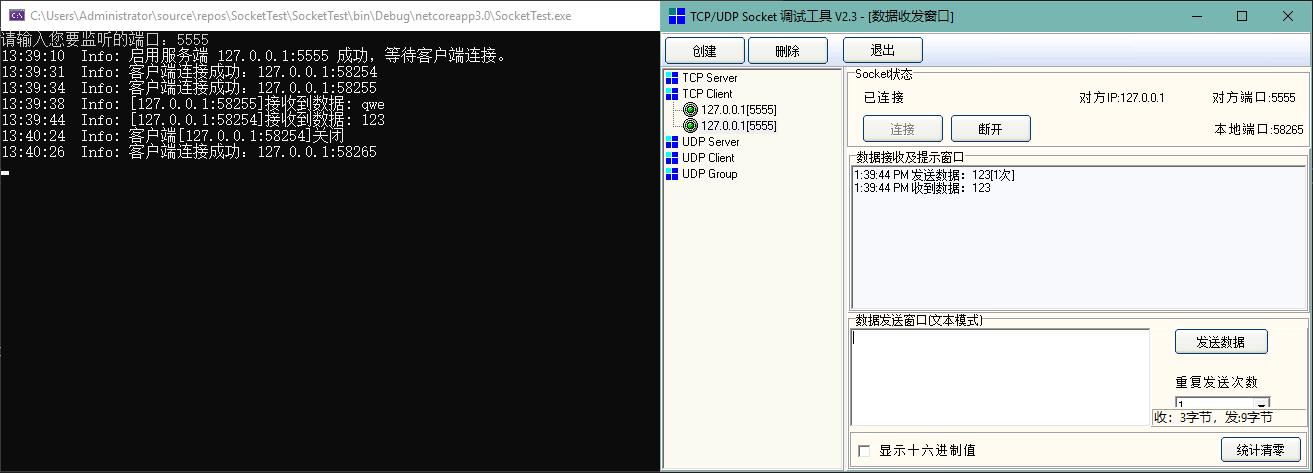
使用while循环,配合AcceptTcpClient方法,不停的监听来自客户端的请求。
循环中,一旦客户端连接成功,开启一个线程处理服务端与客户端的数据交互。然后循环继续,等待下一个客户端连接。
这里我们将测试用例中的Test方法进行改写:
public static void Test()
{
// 服务端地址默认本地
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
// 提醒用户输入要监听的端口
Console.Write("请输入您要监听的端口:");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int port;
while (!int.TryParse(input, out port))
{
Console.Write("您输入的端口错误,请重新输入:");
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
try
{
// 创建并打开监听
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(address, port);
listener.Start();
ConsoleLogger.Info($"启用服务端 {listener.Server.LocalEndPoint} 成功,等待客户端连接。");
// 等待客户端的连接请求
while (true)
{
TcpClient client = listener.AcceptTcpClient();
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端连接成功:{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()}");
// 建立与客户端的数据流
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
using NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];//设置缓存长度
while (true)
{
try
{
int length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
if (length > 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]接收到数据: {Console.InputEncoding.GetString(buffer, 0, length)}");
// 回发接收到的消息给客户端
client.Client.Send(buffer, 0, length, SocketFlags.None);
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]关闭");
break;
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]引发未处理异常:{exc.Message}");
break;
}
}
});
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"TCP服务端测试出现了未经处理的异常:{exc.Message}");
}
ConsoleLogger.Info("测试结束");
}
测试效果如下:
递归
递归本质上和循环类似,其利用的是异步等待TCP客户端连接方法BeginAcceptTcpClient的回调。
我们可以在回调中,使用EndAcceptTcpClient来异步的接受传入的连接,并创建客户端实例。而创建成功后,我们可以继续调用回调函数,来异步的接收下一个客户端的连接请求。
下面例子将回调函数写为匿名函数,实际开发中也可以使用普通函数:
public static void Test()
{
// 服务端地址默认本地
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
// 提醒用户输入要监听的端口
Console.Write("请输入您要监听的端口:");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int port;
while (!int.TryParse(input, out port))
{
Console.Write("您输入的端口错误,请重新输入:");
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
try
{
// 创建并打开监听
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(address, port);
listener.Start();
ConsoleLogger.Info($"启用服务端 {listener.Server.LocalEndPoint} 成功,等待客户端连接。");
// 异步等待客户端的连接请求的回调
AsyncCallback callback = null;
callback = new AsyncCallback((asyncResult) =>
{
// 因为没有使用函数而是使用匿名方法 这里也可以直接用可以访问到的局部变量listener
if (asyncResult.AsyncState is TcpListener tcpListener)
{
TcpClient client = tcpListener.EndAcceptTcpClient(asyncResult);
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端连接成功:{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()}");
// 建立与客户端的数据流
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
using NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];//设置缓存长度
while (true)
{
try
{
int length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
if (length > 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]接收到数据: {Console.InputEncoding.GetString(buffer, 0, length)}");
// 回发接收到的消息给客户端
client.Client.Send(buffer, 0, length, SocketFlags.None);
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]关闭");
break;
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]引发未处理异常:{exc.Message}");
break;
}
}
});
tcpListener.BeginAcceptTcpClient(callback, tcpListener);
}
});
// 异步等待客户端的连接请求
listener.BeginAcceptTcpClient(callback, listener);
Console.ReadKey();//避免控制台退出
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"TCP服务端测试出现了未经处理的异常:{exc.Message}");
}
ConsoleLogger.Info("测试结束");
}
测试效果如下:
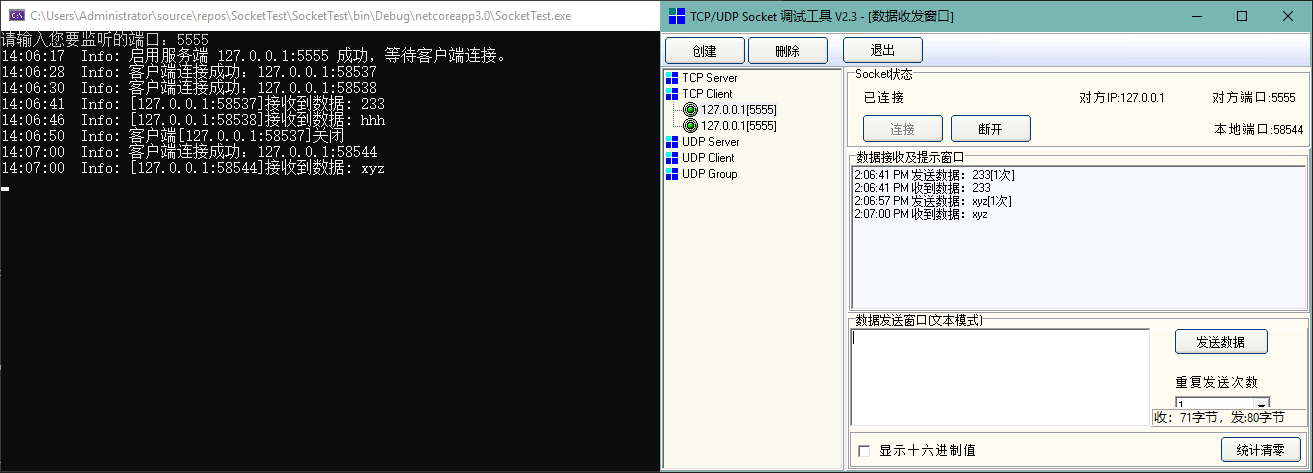
由上图可以看出两者差别并不大,主要的区别在于循环是一个同步方法,而递归使用的是异步方法。
向指定客户端发送消息
控制台中如果控制向客户端发送消息,肯定要允许我们输入,来客户端并可以输入需要发送的消息。
所以这里我们需要将等待客户端连接请求与提示输入放在两个线程中进行,这里我们直接使用多客户端中“递归”的例子进行改造(当然也可以使用循环的例子,开启一个线程将循环放到另外一个线程中执行)。
因为我们的测试方法是静态方法,所以首先我们需要定义一个静态集合变量来存储连接的客户端。
客户端连接成功后,我们需要将客户端存储到集合中,方便我们遍历,当客户端断开连接后,我们需要将客户端从该集合中移除。因为涉及到多线程,这里建议使用线程安全的集合,或者在操作集合的位置加锁。
调整后代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SocketTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TcpServerTest.Test();
}
}
public static class TcpServerTest
{
static readonly object sync = new object();
static List<TcpClient> clients = new List<TcpClient>();
public static void Test()
{
// 服务端地址默认本地
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
// 提醒用户输入要监听的端口
Console.Write("请输入您要监听的端口:");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int port;
while (!int.TryParse(input, out port))
{
Console.Write("您输入的端口错误,请重新输入:");
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
try
{
// 创建并打开监听
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(address, port);
listener.Start();
ConsoleLogger.Info($"启用服务端 {listener.Server.LocalEndPoint} 成功,等待客户端连接。");
// 异步等待客户端的连接请求的回调
AsyncCallback callback = null;
callback = new AsyncCallback((asyncResult) =>
{
// 因为没有使用函数而是使用匿名方法 这里也可以直接用可以访问到的局部变量listener
if (asyncResult.AsyncState is TcpListener tcpListener)
{
TcpClient client = tcpListener.EndAcceptTcpClient(asyncResult);
lock (sync)
{
clients.Add(client);
}
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端连接成功:{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()}");
// 建立与客户端的数据流
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
using NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];//设置缓存长度
while (true)
{
try
{
int length = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
if (length > 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Receive($"[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]接收到数据: {Console.InputEncoding.GetString(buffer, 0, length)}");
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]关闭");
lock (sync)
{
if (clients.Contains(client))
{
clients.Remove(client);
}
}
break;
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"客户端[{client.Client.RemoteEndPoint}]引发未处理异常:{exc.Message}");
lock (sync)
{
if (clients.Contains(client))
{
clients.Remove(client);
}
}
break;
}
}
});
tcpListener.BeginAcceptTcpClient(callback, tcpListener);
}
});
// 异步等待客户端的连接请求
listener.BeginAcceptTcpClient(callback, listener);
while (true)
{
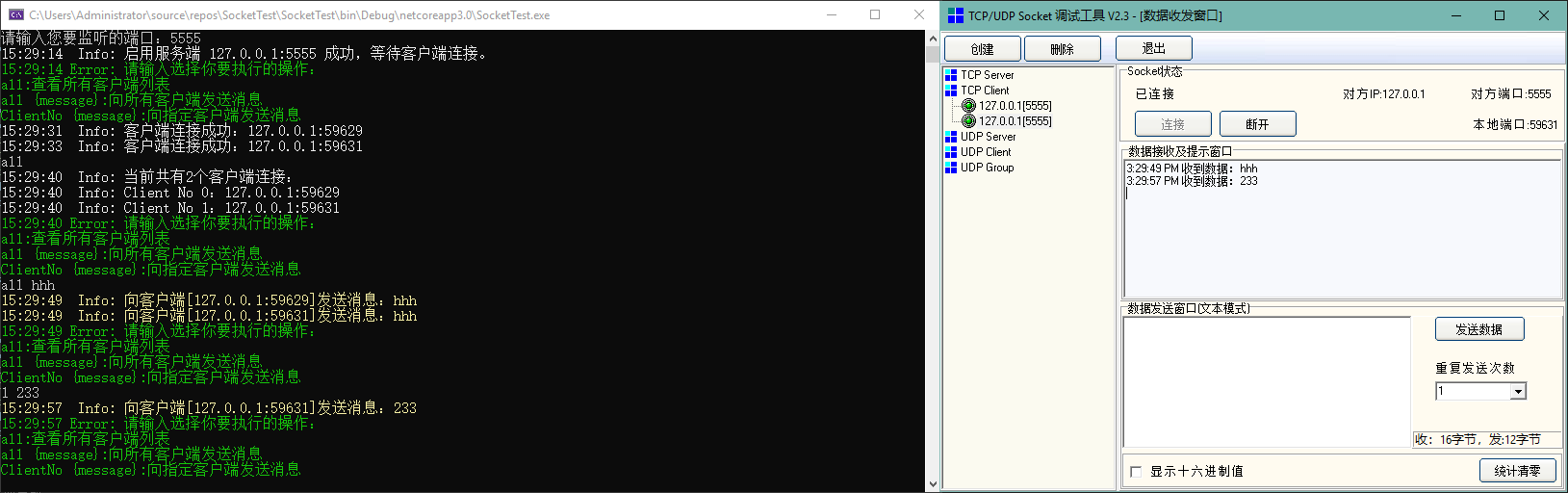
ConsoleLogger.Prompt("请输入选择你要执行的操作:\r\nall:查看所有客户端列表\r\nall {message}:向所有客户端发送消息\r\nClientNo {message}:向指定客户端发送消息");
input = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.Equals(input, "all", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
lock (sync)
{
if (clients.Count == 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"当前还未与客户端建立连接。");
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"当前共有{clients.Count}个客户端连接:");
for (int i = 0; i < clients.Count; i++)
{
ConsoleLogger.Info($"Client No {i}:{clients[i].Client.RemoteEndPoint}");
}
}
}
}
else if (Regex.IsMatch(input, "^all (.+)$", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase))
{
Match match = Regex.Match(input, "^all (.+)$", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase);
string message = match.Groups[1].Value;
lock (sync)
{
if (clients.Count == 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"当前还未与客户端建立连接。");
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < clients.Count; i++)
{
try
{
ConsoleLogger.Send($"向客户端[{clients[i].Client.RemoteEndPoint}]发送消息:{message}");
clients[i].Client.Send(Console.InputEncoding.GetBytes(message));
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"向客户端[{clients[i].Client.RemoteEndPoint}]发送消息失败:{exc.Message}");
}
}
}
}
}
else if (Regex.IsMatch(input, "^(\\d{1,7}) (.+)$", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase))
{
Match match = Regex.Match(input, "^(\\d{1,7}) (.+)$", RegexOptions.IgnoreCase);
int clientIndex = int.Parse(match.Groups[1].Value);
string message = match.Groups[2].Value;
lock (sync)
{
if (clients.Count == 0)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"当前还未与客户端建立连接。");
}
else
{
if (clients.Count > clientIndex)
{
try
{
ConsoleLogger.Send($"向客户端[{clients[clientIndex].Client.RemoteEndPoint}]发送消息:{message}");
clients[clientIndex].Client.Send(Console.InputEncoding.GetBytes(message));
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"向客户端[{clients[clientIndex].Client.RemoteEndPoint}]发送消息失败:{exc.Message}");
}
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"该索引对应的客户端不存在,可能已经被断开连接。");
}
}
}
}
else
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"内容输入错误,请按照要求重新输入你要进行的操作。");
}
}
}
catch (Exception exc)
{
ConsoleLogger.Error($"TCP服务端测试出现了未经处理的异常:{exc.Message}");
}
ConsoleLogger.Info("测试结束");
}
}
public class ConsoleLogger
{
private static readonly object sync = new object();
public static void Send(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} Info: {message}");
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
public static void Receive(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} Info: {message}");
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
public static void Prompt(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
public static void Error(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} Error: {message}");
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
public static void Info(string message)
{
lock (sync)
{
ConsoleColor backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
ConsoleColor foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} Info: {message}");
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor;
}
}
}
}
测试效果如下: