简述表达式目录树
简单的表达式树实现以及声明方式
下面的代码分别是 Lambda 表达式与表达式目录树的 Lambda 表达方式:
Console.WriteLine("***Lambda表达式***");
{
Func<int, int, int> func = (m, n) => (m + n) * 2;
var result = func(55, 66);
Console.WriteLine($"lambda:{result}");
}
Console.WriteLine("***Lambda表达式目录树***");
{
Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = (m, n) => (m + n) * 2;
// var func = expression.Compile();
// var result = func(55, 66);
var result = expression.Compile()(55, 66);
Console.WriteLine($"expression:{result}");
}
执行结果:

同样我们也可以拼装一个表达式目录树:
Console.WriteLine("***拼装表达式目录树***"); // 自己拼装表达式目录树
{
ParameterExpression parameterExpression1 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "m");// 参数表达式
ParameterExpression parameterExpression2 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "n");
ConstantExpression constantExpression = Expression.Constant(2);// 常量表达式
BinaryExpression binaryExpression1 = Expression.Add(parameterExpression1, parameterExpression2);// 二元表达式
BinaryExpression binaryExpression2 = Expression.Multiply(binaryExpression1, constantExpression);
Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(binaryExpression2, parameterExpression1, parameterExpression2);// 将表达式翻译生 lambda 表达式 并将参数表达式传入
var result = expression.Compile()(55, 66);
Console.WriteLine($"expression:{result}");
}
执行结果:

使用工具查看表达式目录树结构
首先安装 ExpressionTreeVisualizer 工具,将不同版本的 ExpressionTreeVisualizer.dll 文件放置到对应版本的 VS 调试工具目录下,比如 Visual Studio 2017 需要放置到:C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Enterprise\Common7\Packages\Debugger\Visualizers目录下。
文件拷贝到指定目录后,需要重启 Visual Studio,重启后调试程序,表达式目录树的监视工具会有一个 Expression Tree Visualizer 的选项。

选择该工具进行查看,可以看到表达式目录树的结构。
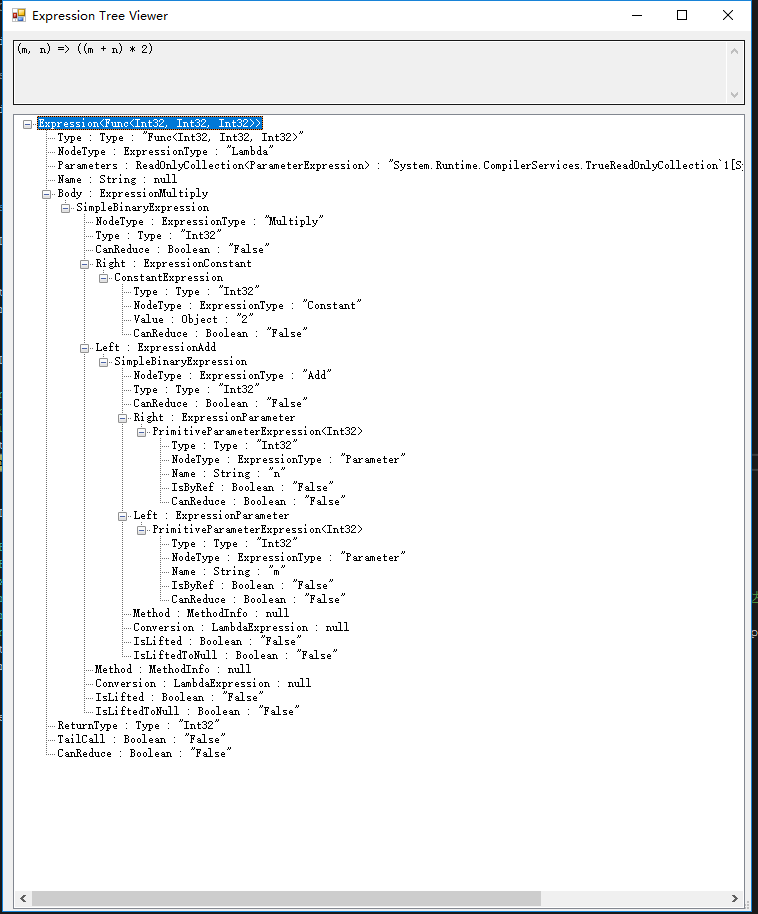
我们通过该工具的目录树结构,对 Lambda 表达式目录树进行分拆。
表达式目录树过滤对象
实体 User 类:
using System;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public int? Age { get; set; }
public DateTime? CreateDate { get; set; }
}
}
使用 EF 查询:
List<User> users = new List<User>()
{
new User() { Id = 1, Name = "Kangkang", Email = "kangkang@qq.com", Age = 17 },
new User() { Id = 2, Name = "Jane", Email = "jane@yahoo.com", Age = 16 },
new User() { Id = 3, Name = "Mike", Email = "mike@google.com", Age = 17 },
new User() { Id = 4, Name = "John", Email = "john@outlook.com", Age = 19 },
new User() { Id = 5, Name = "Lili", Email = "lili@163.com", Age = 18 },
};
string name = "Kangkang";
string emailType = "@qq.com";
int? minAge = 15;
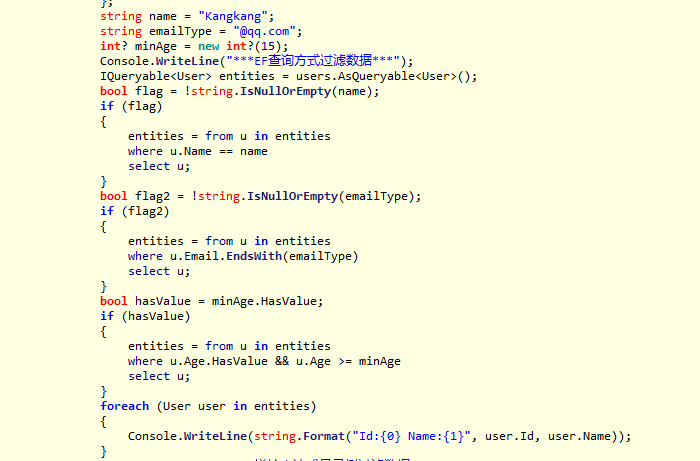
Console.WriteLine("***EF查询方式过滤数据***");
{
var entities = users.AsQueryable();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
entities = entities.Where(u => u.Name == name);
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(emailType))
{
entities = entities.Where(u => u.Email.EndsWith(emailType));
}
if (minAge.HasValue)
{
entities = entities.Where(u => u.Age.HasValue && u.Age >= minAge);
}
foreach (var user in entities)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{user.Id} Name:{user.Name}");
}
}
拼装表达式目录树:
Console.WriteLine("***拼接表达式目录树过滤数据***");
{
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u");
Expression<Func<User, bool>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(Expression.Constant(true), parameterExpression);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
MemberExpression memberExpression = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(User).GetProperty("Name"));
ConstantExpression constantExpression = Expression.Constant(name);
// 使用 Equal 方法
BinaryExpression binaryExpression = Expression.Equal(memberExpression, constantExpression);
Expression<Func<User, bool>> expressionName = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(binaryExpression, parameterExpression);
// // 使用 Call 方法
// MethodInfo methodInfo = typeof(string).GetMethod("Equals", new Type[] { typeof(string) });
// MethodCallExpression methodCallExpression = Expression.Call(memberExpression, methodInfo, constantExpression);
// Expression<Func<User, bool>> expressionName = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(methodCallExpression, parameterExpression);
// 合并表达式目录树
expression = expression.And(expressionName);
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(emailType))
{
MemberExpression memberExpression = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(User).GetProperty("Email"));
ConstantExpression constantExpression = Expression.Constant(emailType);
// 使用 Call 方法
MethodInfo methodInfo = typeof(string).GetMethod("EndsWith", new Type[] { typeof(string) });
MethodCallExpression methodCallExpression = Expression.Call(memberExpression, methodInfo, constantExpression);
Expression<Func<User, bool>> expressionEmailType = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(methodCallExpression, parameterExpression);
// 合并表达式目录树
expression = expression.And(expressionEmailType);
}
if (minAge.HasValue)
{
Expression<Func<User, bool>> expressionAge = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(Expression.Property(Expression.Property(Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u"), typeof(User).GetProperty("Age")), typeof(int?).GetProperty("HasValue")), Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u"));
// 合并表达式目录树
expression = expression.And(expressionAge);
BinaryExpression binaryExpression = Expression.GreaterThanOrEqual(Expression.Property(Expression.Property(Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u"), typeof(User).GetProperty("Age")), typeof(int?).GetProperty("Value")), Expression.Constant(minAge, typeof(int)));
expressionAge = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(binaryExpression, parameterExpression);
// 合并表达式目录树
expression = expression.And(expressionAge);
}
foreach (var user in users.AsQueryable().Where(expression))
{
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{user.Id} Name:{user.Name}");
}
}
上面拼装涉及到的合并表达式目录树:
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
/// <summary>
/// 遍历表达式类型 当遇到参数类型表达式时 替换为我们自己定义的参数
/// </summary>
public class ExpressionVisitorExtend : ExpressionVisitor
{
public ParameterExpression Parameter { get; private set; }
public ExpressionVisitorExtend(ParameterExpression param)
{
this.Parameter = param;
}
public Expression Replace(Expression exp)
{
return this.Visit(exp);
}
protected override Expression VisitParameter(ParameterExpression node)
{
return this.Parameter;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public static class ExpressionExtend
{
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> And<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr1, Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr2)
{
if (expr1 == null)
return expr2;
else if (expr2 == null)
return expr1;
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "t");
ExpressionVisitorExtend visitor = new ExpressionVisitorExtend(parameterExpression);
var left = visitor.Replace(expr1.Body);
var right = visitor.Replace(expr2.Body);
var body = Expression.And(left, right);
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>(body, parameterExpression);
}
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> Or<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr1, Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr2)
{
if (expr1 == null)
return expr2;
else if (expr2 == null)
return expr1;
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "t");
ExpressionVisitorExtend visitor = new ExpressionVisitorExtend(parameterExpression);
var left = visitor.Replace(expr1.Body);
var right = visitor.Replace(expr2.Body);
var body = Expression.Or(left, right);
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>(body, parameterExpression);
}
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> Not<T>(this Expression<Func<T, bool>> expr)
{
if (expr == null)
return null;
var candidateExpr = expr.Parameters[0];
var body = Expression.Not(expr.Body);
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>(body, candidateExpr);
}
}
}
注意: EF 中使用 Lambda 表达式目录树其实是语法糖,通过 ILSpy 或者 Reflactor 等反编译工具我们可以看到实际的代码,比如:
entities = entities.Where(u => u.Age.HasValue && u.Age >= minAge);
反编译后内容是:
ParameterExpression[] expressionArray4 = new ParameterExpression[] { expression };
queryable = queryable.Where<User>(Expression.Lambda<Func<User, bool>>(Expression.AndAlso(Expression.Property(Expression.Property(expression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u"), (MethodInfo) methodof(User.get_Age)), (MethodInfo) methodof(int?.get_HasValue, int?)), Expression.GreaterThanOrEqual(Expression.Property(expression, (MethodInfo) methodof(User.get_Age)), Expression.Field(Expression.Constant(class_, typeof(<>c__DisplayClass0_0)), fieldof(<>c__DisplayClass0_0.minAge)))), expressionArray4));
当然上面代码中有些变量被反编译到其他位置,这里不再一一写出,而且这些内容在 VS 并不能被编译通过,所以如果想通过反编译工具将 Lambda 表达式目录树反拆出拼装的语句,需要再“翻译”一下。
另外这些语法糖并不是所有的反编译工具都能识别到,比如我在一个版本的 ILSpay 中打开这个项目的代码,还是语法糖的形式,但是在 .NET Reflector 中就可以查看到反编译后的内容。
ILSpy 中查看到的反编译内容:
.NET Reflector 中查看的反编译内容:

更多内容可以查看文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/jesse2013/p/expressiontree-part1.html
类型转换
需求描述
日常工作中经常会有需求,将一个类型的属性和字段值赋值给另外一个类型,两个类型的结构基本一致。例如:
User.cs
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public int? Age { get; set; }
public DateTime? CreateDate { get; set; }
}
UserCopy.cs
public class UserCopy
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
}
实现方案
硬编码
简单粗暴的方式:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public class ObjectMapper
{
/// <summary>
/// 硬编码的类型转换方案
/// </summary>
/// <param name="user"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static UserCopy TransUserCopy(User user)
{
return new UserCopy()
{
Id = user.Id,
Name = user.Name,
Email = user.Email
};
}
}
}
调用:
User user = new User() { Id = 1, Name = "Kangkang", Email = "kangkang@qq.com", Age = 17, CreateDate = new DateTime(2015, 1, 1) };
Console.WriteLine("***硬编码做法***");
{
// 效率最高但是最不灵活 比如其他类型的转换需要新建方法 属性值变化或者属性值较多比较麻烦
UserCopy copy = ObjectMapper.TransUserCopy(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
序列化
需要引用 Newtonsoft.Json:
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public class SerializeMapper
{
/// <summary>
/// 序列化方式实现类型转换
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam>
/// <param name="tIn"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn)
{
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TOut>(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(tIn));
}
}
}
调用:
User user = new User() { Id = 1, Name = "Kangkang", Email = "kangkang@qq.com", Age = 17, CreateDate = new DateTime(2015, 1, 1) };
Console.WriteLine("***序列化转换***");
{
UserCopy copy = SerializeMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
反射
反射是常用做法:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public class ReflectionMapper
{
/// <summary>
/// 反射方式实现类型转换
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TIn"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TOut"></typeparam>
/// <param name="tIn"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn)
{
List<FieldInfo> tInFields = typeof(TIn).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tInProps = typeof(TIn).GetProperties().ToList();
List<FieldInfo> tOutFields = typeof(TOut).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tOutProps = typeof(TOut).GetProperties().ToList();
TOut tOut = Activator.CreateInstance<TOut>();
foreach (var field in tOutFields)
{
var tempField = tInFields.Find(f => f.Name == field.Name && f.FieldType == field.FieldType);
if (tempField != null)
{
field.SetValue(tOut, tempField.GetValue(tIn));
}
}
foreach (var prop in tOutProps)
{
var tempProp = tInProps.Find(p => p.Name == prop.Name && p.PropertyType == prop.PropertyType);
if (tempProp != null)
{
prop.SetValue(tOut, tempProp.GetValue(tIn, null), null);
}
}
return tOut;
}
}
}
调用:
User user = new User() { Id = 1, Name = "Kangkang", Email = "kangkang@qq.com", Age = 17, CreateDate = new DateTime(2015, 1, 1) };
Console.WriteLine("***反射转换***");
{
UserCopy copy = ReflectionMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
表达式目录树
首先需要理解一下表达式目录树如何实现转换:
User user = new User() { Id = 1, Name = "Kangkang", Email = "kangkang@qq.com", Age = 17, CreateDate = new DateTime(2015, 1, 1) };
Console.WriteLine("***Lambda表达式目录树模仿硬编码***");
{
Expression<Func<User, UserCopy>> expression = u => new UserCopy() { Id = u.Id, Name = u.Name, Email = u.Email };
UserCopy copy = expression.Compile()(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
将 Lambda 表达式目录树进行拆解,观察是否有规律可循:
Console.WriteLine("***拼装表达式目录树模仿硬编码***");
{
// 可以通过反编译工具模仿 Lambda 表达式目录树
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u");
MemberBinding[] bindings = new MemberBinding[] { Expression.Bind(typeof(UserCopy).GetProperty("Id"), Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(User).GetProperty("Id"))), Expression.Bind(typeof(UserCopy).GetProperty("Name"), Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(User).GetProperty("Name"))), Expression.Bind(typeof(UserCopy).GetProperty("Email"), Expression.Property(parameterExpression, typeof(User).GetProperty("Email"))) };
Expression<Func<User, UserCopy>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, UserCopy>>(Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(UserCopy)), bindings), parameterExpression);
UserCopy copy = expression.Compile()(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
结合反射组装表达式目录树:
Console.WriteLine("***通过反射拼接表达式目录树***");
{
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(User), "u");
List<MemberBinding> bindings = new List<MemberBinding>();
List<FieldInfo> tUserFields = typeof(User).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tUserProps = typeof(User).GetProperties().ToList();
List<FieldInfo> tCopyFields = typeof(UserCopy).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tCopyProps = typeof(UserCopy).GetProperties().ToList();
foreach (var field in tCopyFields)
{
var tempField = tUserFields.Find(f => f.Name == field.Name && f.FieldType == field.FieldType);
if (tempField != null)
{
bindings.Add(Expression.Bind(field, Expression.Field(parameterExpression, tempField)));
}
}
foreach (var prop in tCopyProps)
{
var tempProp = tUserProps.Find(p => p.Name == prop.Name && p.PropertyType == prop.PropertyType);
if (tempProp != null)
{
bindings.Add(Expression.Bind(prop, Expression.Property(parameterExpression, tempProp)));
}
}
Expression<Func<User, UserCopy>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<User, UserCopy>>(Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(UserCopy)), bindings), parameterExpression);
UserCopy copy = expression.Compile()(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
表达式目录树编译后的委托类型可以缓存,提高程序效率:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public class ExpressionMapper
{
private static Dictionary<string, Delegate> _Dic = new Dictionary<string, Delegate>();
public static TOut Trans<TIn, TOut>(TIn tIn)
{
string funcKey = $"{typeof(TIn).GetType().FullName}${typeof(TOut).FullName}";
if (!_Dic.ContainsKey(funcKey))
{
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TIn), "t");
List<MemberBinding> bindings = new List<MemberBinding>();
List<FieldInfo> tUserFields = typeof(TIn).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tUserProps = typeof(TIn).GetProperties().ToList();
List<FieldInfo> tCopyFields = typeof(TOut).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tCopyProps = typeof(TOut).GetProperties().ToList();
foreach (var field in tCopyFields)
{
var tempField = tUserFields.Find(f => f.Name == field.Name && f.FieldType == field.FieldType);
if (tempField != null)
{
bindings.Add(Expression.Bind(field, Expression.Field(parameterExpression, tempField)));
}
}
foreach (var prop in tCopyProps)
{
var tempProp = tUserProps.Find(p => p.Name == prop.Name && p.PropertyType == prop.PropertyType);
if (tempProp != null)
{
bindings.Add(Expression.Bind(prop, Expression.Property(parameterExpression, tempProp)));
}
}
Expression<Func<TIn, TOut>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<TIn, TOut>>(Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TOut)), bindings), parameterExpression);
_Dic[funcKey] = expression.Compile();
}
return ((Func<TIn, TOut>)_Dic[funcKey]).Invoke(tIn);
}
}
}
结合泛型部分学习到的泛型缓存知识,使用泛型作为缓存载体取代字典:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
namespace JohnSun.ExpressionTest.ConsoleApp
{
public class ExpressionGenericMapper<TIn, TOut>
{
private static Func<TIn, TOut> _Func = null;
static ExpressionGenericMapper()
{
ParameterExpression parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TIn), "t");
List<MemberBinding> bindings = new List<MemberBinding>();
List<FieldInfo> tUserFields = typeof(TIn).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tUserProps = typeof(TIn).GetProperties().ToList();
List<FieldInfo> tCopyFields = typeof(TOut).GetFields().ToList();
List<PropertyInfo> tCopyProps = typeof(TOut).GetProperties().ToList();
foreach (var field in tCopyFields)
{
var tempField = tUserFields.Find(f => f.Name == field.Name && f.FieldType == field.FieldType);
if (tempField != null)
{
bindings.Add(Expression.Bind(field, Expression.Field(parameterExpression, tempField)));
}
}
foreach (var prop in tCopyProps)
{
var tempProp = tUserProps.Find(p => p.Name == prop.Name && p.PropertyType == prop.PropertyType);
if (tempProp != null)
{
bindings.Add(Expression.Bind(prop, Expression.Property(parameterExpression, tempProp)));
}
}
Expression<Func<TIn, TOut>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<TIn, TOut>>(Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(typeof(TOut)), bindings), parameterExpression);
_Func = expression.Compile();
}
public static TOut Trans(TIn tIn)
{
return _Func.Invoke(tIn);
}
}
}
调用:
Console.WriteLine("***通过反射拼接表达式目录树(缓存扩展)***");
{
// 第一次调用生成对应类型转换的委托后面再调用直接使用委托转换 提高转换效率
UserCopy copy = ExpressionMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
copy = ExpressionMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
Console.WriteLine("***通过反射拼接表达式目录树(泛型缓存扩展)***");
{
// 泛型类由于类型不同 会生成一个全新的副本 实现缓存的效果
UserCopy copy = ExpressionGenericMapper<User, UserCopy>.Trans(user);
copy = ExpressionGenericMapper<User,UserCopy>.Trans(user);
Console.WriteLine($"Id:{copy.Id} Name:{copy.Name} Email:{copy.Email}");
}
测试不同方法进行类型转换的效率
测试部分代码:
long time = 0;
User user = new User() { Id = 1, Name = "Kangkang", Email = "kangkang@qq.com", Age = 17, CreateDate = new DateTime(2015, 1, 1) };
Console.WriteLine("***硬编码转换***");
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
int sum = 0;
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
UserCopy copy = ObjectMapper.TransUserCopy(user);
sum += copy.Id;
}
watch.Stop();
time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine($"***硬编码转换 {time}ms***");
Console.WriteLine("***序列化转换***");
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
int sum = 0;
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
UserCopy copy = SerializeMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
sum += copy.Id;
}
watch.Stop();
time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine($"***序列化转换 {time}ms***");
Console.WriteLine("***反射转换***");
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
int sum = 0;
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
UserCopy copy = ReflectionMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
sum += copy.Id;
}
watch.Stop();
time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine($"***反射转换 {time}ms***");
Console.WriteLine("***表达式目录树结合缓存***");
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
int sum = 0;
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
UserCopy copy = ExpressionMapper.Trans<User, UserCopy>(user);
sum += copy.Id;
}
watch.Stop();
time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine($"***表达式目录树结合缓存 {time}ms***");
Console.WriteLine("***表达式目录树结合泛型缓存***");
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
int sum = 0;
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
UserCopy copy = ExpressionGenericMapper<User,UserCopy>.Trans(user);
sum += copy.Id;
}
watch.Stop();
time = watch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine($"***表达式目录树结合泛型缓存 {time}ms***");
执行结果:
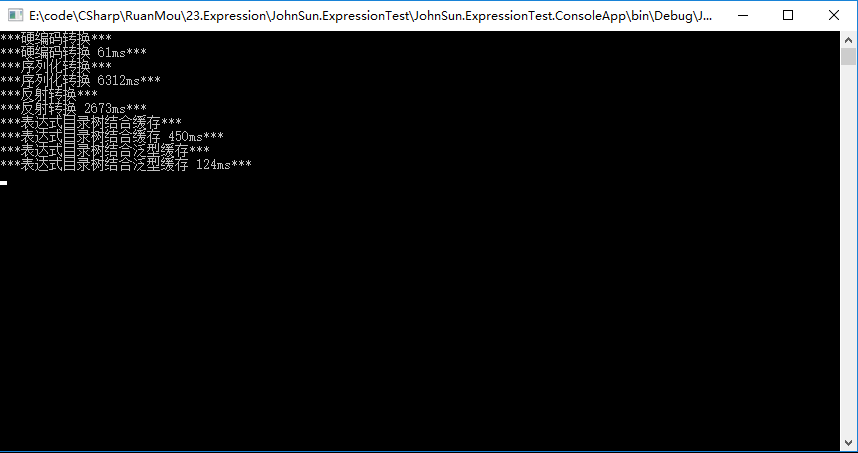
结合结果,明显可取的方案为表达式目录树结合泛型缓存进行转换,其耗时与硬编码最接近。